-
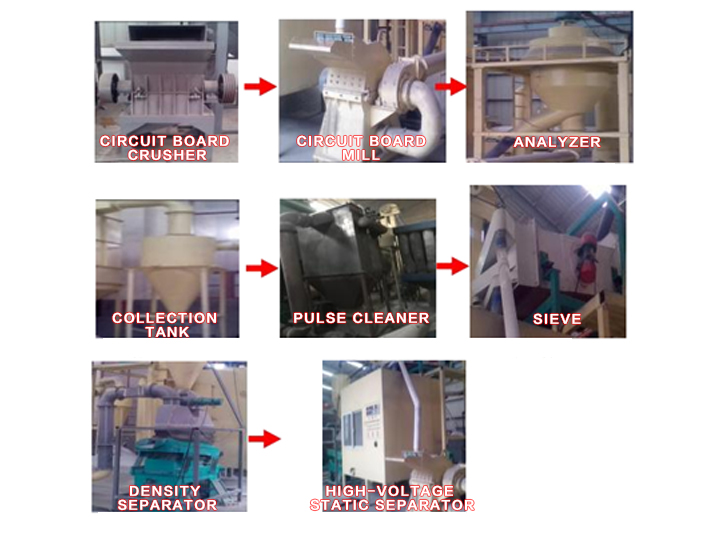 circuit board crushing、screening、static Separator
circuit board crushing、screening、static Separator1、Circuit Board Crusher: Breaks the circuit board to crush into pieces 2-3 cm in length.
2、Circuit Board Mill: Pulverizes the crushed circuit boards into particles around 20 mesh.
3、Analyzer: Conducts wind selection on the milled materials, separating resins, copper, dust, and fibers. Dust and fibers are collected by a fan into the collection tank, while resins and copper are fed into the sizing system.
4、Collection Tank: Collects the dust and fibers. Fibers after collection are discharged for disposal.
5、Pulse Cleaner: Collects the dust and fine fibers generated during the breaking process.
6、Sieve: Separates resins and copper. If they do not separate properly, they are returned to the main unit for further milling; separated resins and copper are then fed into the density separation system for sorting.
7、Density Separator: Uses a separation method that takes advantage of the weight difference between copper and resin. Since copper is heavier than resin, it is separated from the other materials, achieving a separation rate of over 99%. This is currently one of the most advanced technologies in the country.
8、High-Voltage Static Separator: Further processes the residues from the density separator using high-voltage static electricity to separate fine copper powder and resins (the principle involves applying high voltage through a transformer to create a magnetic field, which attracts and separates conductive materials like copper).
-
 PCB circuit board precious metal extraction recycling scheme
PCB circuit board precious metal extraction recycling schemeState of Raw Materials and Products:
raw material:Monthly processing capacity: 50 tons of PCB board. Requirements include circuit board desoldering and powderizing leadframe, as well as separation of electronic components.
product:
1、National standard 1# gold;
2、Sponge platinum (≥99.95% purity);
3、Sponge palladium (≥99.95% purity);
4、Rough copper;
5、Resin.
design scheme:
This project processes PCB board scrap through physical and chemical methods to extract and refine precious metal products in accordance with national standards. The precious metal extraction should use simple, mature, and reliable processing methods as much as possible to achieve functional reliability, economic rationality, and management convenience; based on the product positioning of the client's products, combined with our company's precious metal refining and purifying equipment engineering application practice, the initial technical flowchart of the project is as follows.
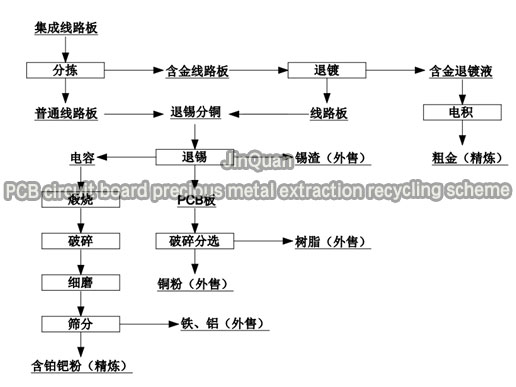
-
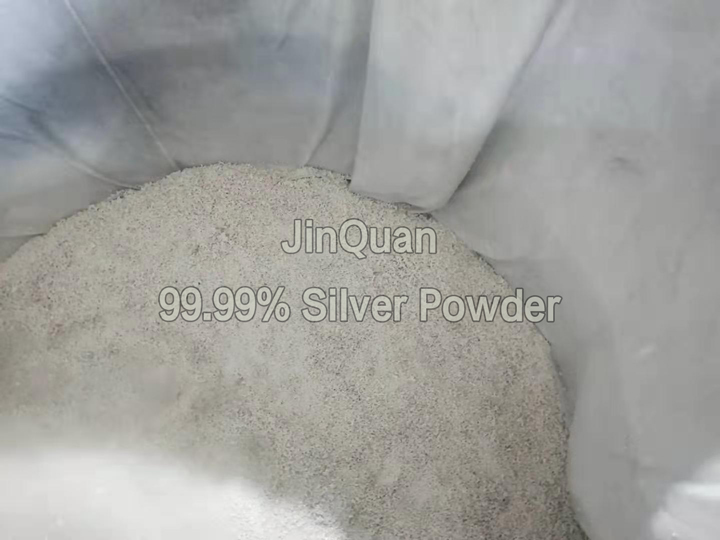 silver-concentrate extraction process
silver-concentrate extraction processMethods of Silver-concentrate Extraction:
Silver refining is often conducted in cyano and thiosulfate solutions, while the use of HCl and HNO3 for silver leaching is limited. In HCl solution, silver primarily exists as AgCl, forming precipitates under high chloride concentrations. Thus, precipitation methods are commonly used to recover silver rather than leaching methods.
In HNO3 solution, silver mainly exists as AgNO3 with a higher solubility. However, nitric acid acts as a strong oxidizer, which can degrade or age the leach solutions. For effective silver leaching, the leaching agents must possess good anti-oxidation properties. As a result, there are very few effective leaching agents for silver.
In cyano compounds, silver reacts similarly to gold, forming complexes like K3[Ag(CN)2]. These can be leached using appropriate cyanide-based leach solutions.
In thiosulfate-containing solutions, silver forms Ag(S₂O₃), which can be leached by specific reagents. -
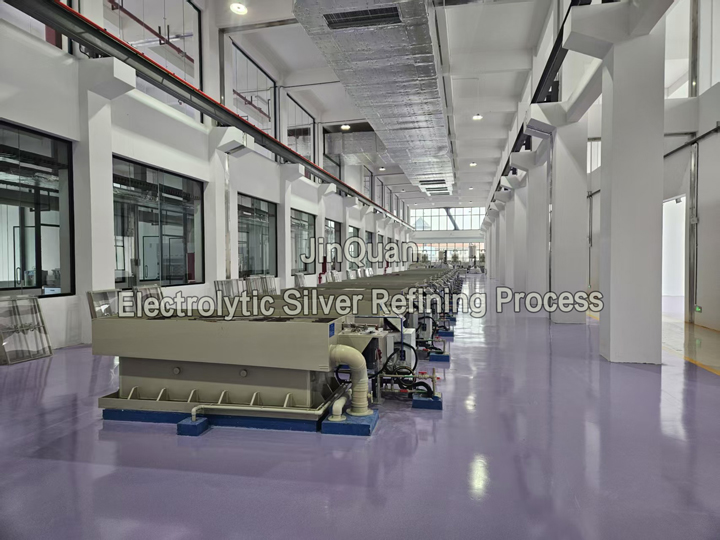 electrolytic silver refining process
electrolytic silver refining processAn electrolytic silver refining process in which crude silver is anodically dissolved and refined silver is cathodically deposited and at the same time accompanying metals are selectively extracted from the spent electrolyte and separately cathodically deposited after having been transferred into an aqueous phase and the regenerated electrolyte stripped of accompanying metals is recycled to the refining process and in which further the spent electrolyte is anodically enriched in silver and accompanying metals are cathodically deposited from the aqueous phase in a joint electrolysis step.
The invention resides in that the joint electrolysis step is carried out in a diaphragm cell in which a diffusion zone is provided between one each cathode and one each anode and separated from the anode zone by an anionic separating membrane and from the cathode zone by a cationic separating membrane and that the diaphragm cell is charged via the diffusion zone with accompanying metal extract.
-
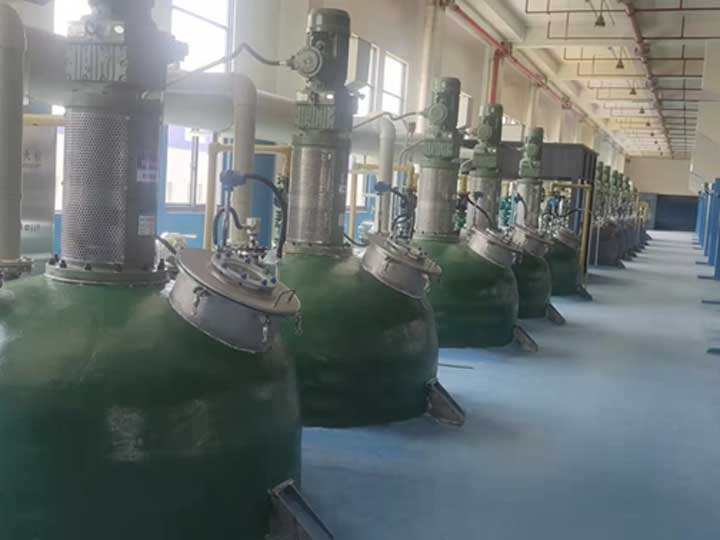 process for refining copper anode slime
process for refining copper anode slimeProcess For Refining Copper Anode Slime.:
1、Sulfuric roasting: recovery of selenium from the fumes;
2、Sulfuric immersion of copper: separation of copper solution and silver, followed by recovery of copper from the silver residue;
3、Alkaline leaching: removal of boric acid from alkaline solutions;
4、Chloride separation of gold: initial gold solution is reduced (the rough gold is refined into fine gold); after reduction, the solution is replaced with palladium and platinum;
5、sodium sulfite separation of silver: sodium sulfite separates silver from sodium sulfite solution; followed by ethanol reduction of rough silver powder;
6、Refining of rough silver: electrorefining of silver
-
 the electrorefining of ultrapure copper
the electrorefining of ultrapure copperThrough controlled electrolytic environments and self-cleaning electrolyte technology, a process and device for electrorefining 6N ultra-pure copper has been developed.
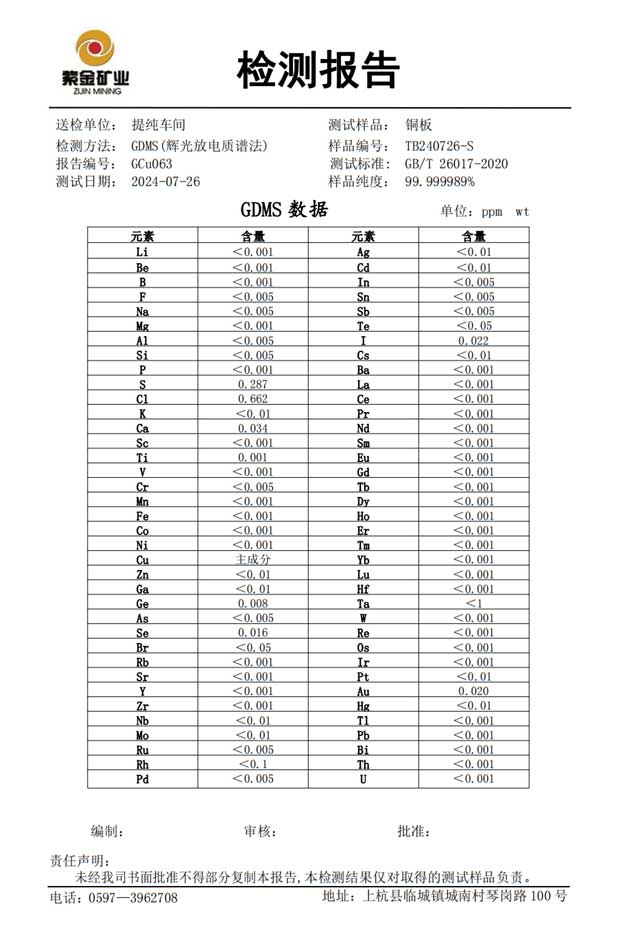
Test Report
-
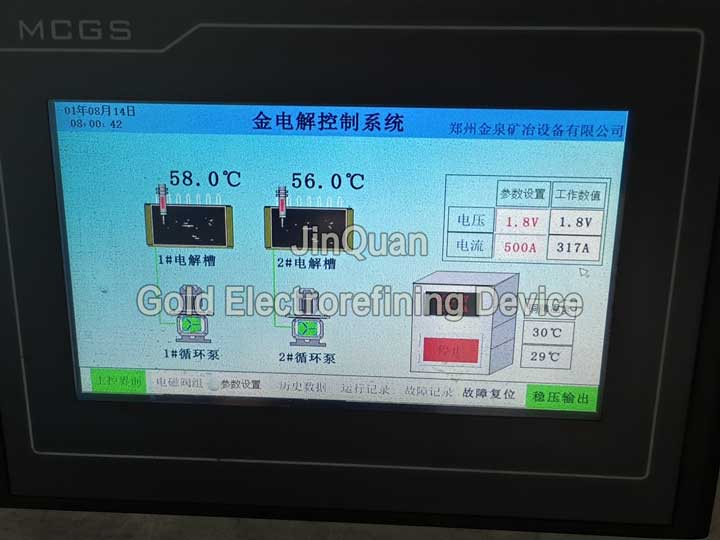 gold electrorefining device
gold electrorefining deviceIntelligent gold electrorefining device designed with integrated and unified design, comprising individual electrolytic cells, circulation pumps, power supply units, automatic electrolyte replenishment systems, smoke gas condensing recovery systems, electrolyte temperature, voltage, current, copper plate temperature intelligent monitoring systems, and data recording systems.
The power supply unit is separately enclosed to isolate acid gases from the workshop, ensuring a long service life。
-
 the process of refining gold production
the process of refining gold productionWith coarse gold as the anode and chloroauric acid solution as the electrolyte, a high current density electroplating process is used to stably produce purity of 99.99% or higher refined gold deposits on the cathode.
The residual electrodes are re-melted after regushing the electrolysis for recasting into high-gold anodes. The platinum-tantalum in the anode sludge is recovered using a wet method. -
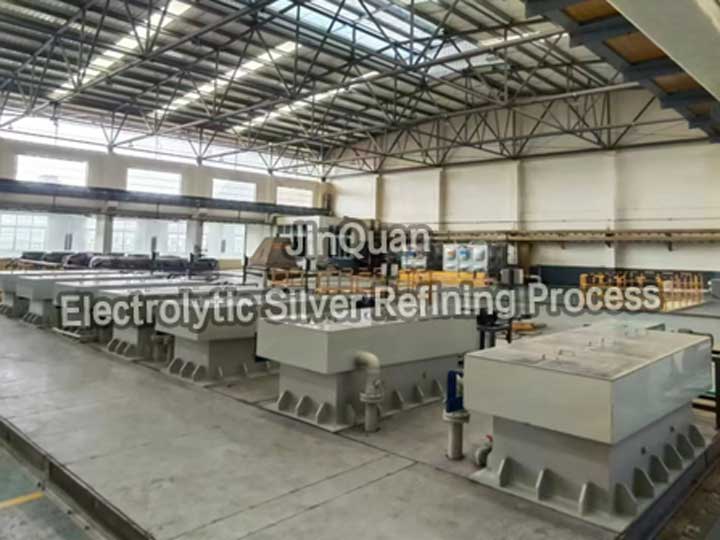 electrolytic silver refining process
electrolytic silver refining processWith coarse silver as the anode and nitric acid silver as the electrolyte, a high current density electroplating process is used to produce silver powder with purity of 99.99% or higher.
After cleaning the residual electrodes, they are placed into the residual electrode bath to directly produce silver powder with purity of 99.99% or higher.
Waste electrolytes undergo oxidation silver purification, and after purification, the qualified electrolytes are returned for recycling.







