 +8613303827570
+8613303827570
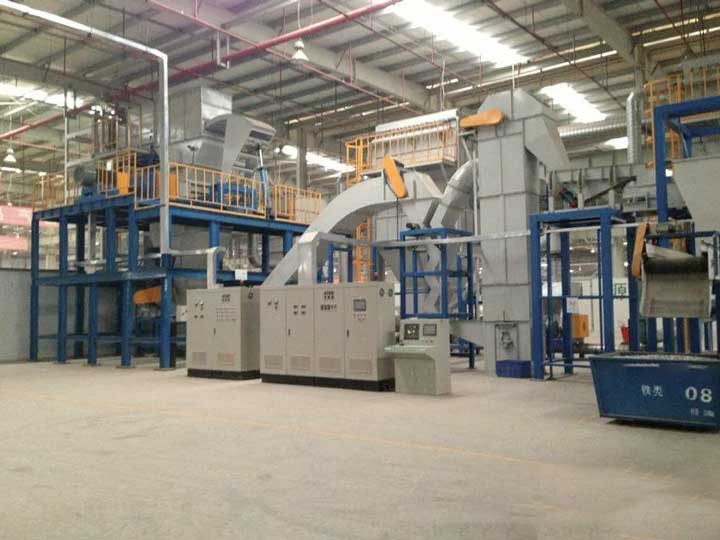
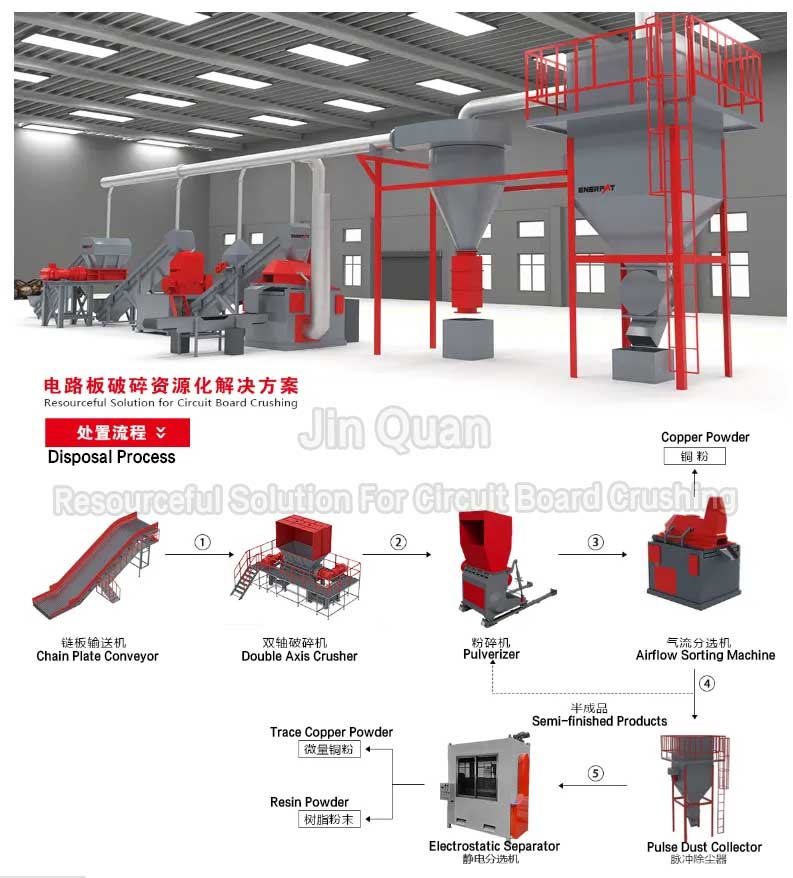
Mainly using methods or based on the differences in physical properties between materials, including density, conductivity, magnetism, surface characteristics, etc. for recycling, including processes such as disassembly, crushing, and sorting. Physical processing technology can enrich valuable substances in electronic waste, with advantages such as low cost and low pollution. However, due to the low proportion of precious metals in the total mass of printed circuit boards, it is difficult to recover high-purity precious metals using general methods. Various physical processing technologies still require subsequent processing of precious metal products. The main physical recycling methods currently used include impact crushing, extrusion crushing, shear crushing, high-speed eddy current crushing, dry screening, air shaking table, magnetic separation, electrostatic separation, pneumatic eddy current separation, and eddy current separation.
Resourceful Solution For Circuit Board Crushing:
-
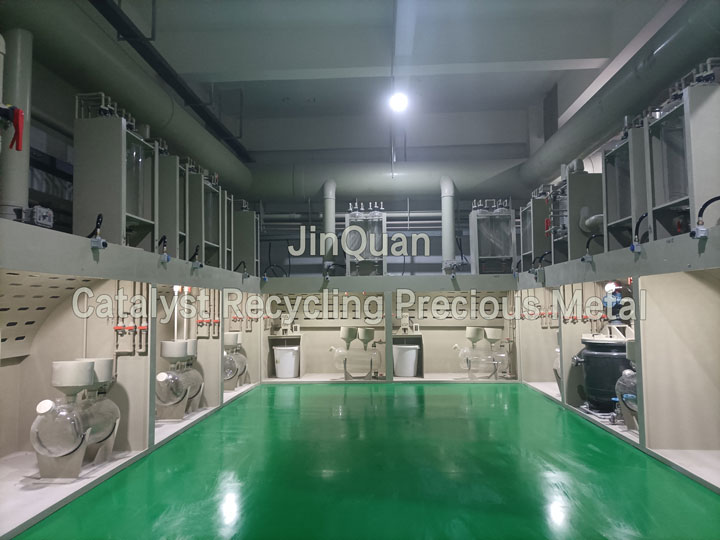 Recovering palladium Carbon Catalyst ProcessRecovering palladium Carbon Catalyst Process
Recovering palladium Carbon Catalyst ProcessRecovering palladium Carbon Catalyst ProcessRecovering palladium Carbon Catalyst Process
Thermal Treatment:The palladium carbon catalyst is immersed in a hot water bath and heated to facilitate the decomposition of organic substances within the catalyst, thereby aiding in its recovery.
Acidic Dissolution:The catalyst is submerged in an acidic solution to leach out palladium ions, reducing the organic content.
Basic Dissolution:The catalyst is treated with a basic solution to extract carbon ions, further decreasing the organic material.
Chloride Solution Treatment:The catalyst is placed in a chloride solution to dissolve metal ions, thereby reducing the organic content.
Leaching with Solvent:The catalyst is immersed in a solvent to absorb and remove organic substances, minimizing their presence within the catalyst.
Recovery of Organic Substances:The extracted organic material is collected for reuse, ensuring minimal waste and maximal efficiency.
High-Temperature Decomposition:The catalyst undergoes high-temperature treatment to ensure complete decomposition of organic substances, facilitating effective recovery.
Vapor Extraction:The catalyst is subjected to vapor processing to extract tantalum ions, enabling their reintegration into the catalyst for reuse.
-
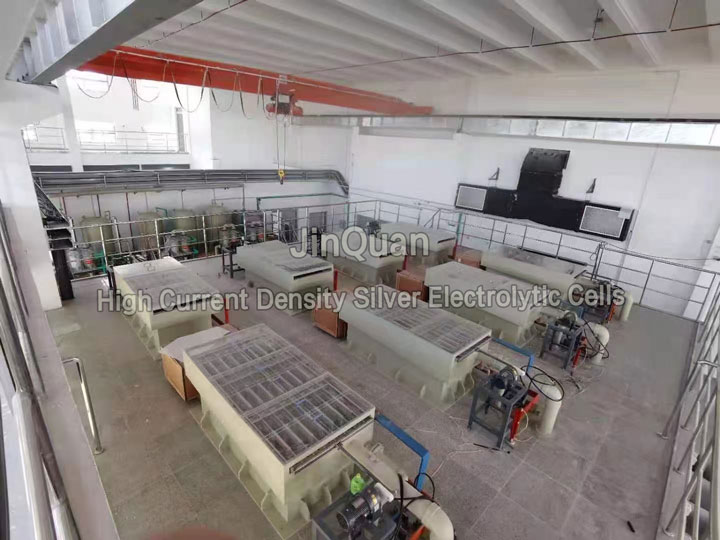 Silver Electrolysis anode slimeHow to Process Silver Electrolysis anode slime
Silver Electrolysis anode slimeHow to Process Silver Electrolysis anode slimeHow to Process Silver Electrolysis anode slime
The anode slime produced during silver electrolysis constitutes about 8% of the anode's weight and typically contains 50%-70% gold and 30%-40% silver, along with minor impurities. Due to the high silver content, this anode slime cannot be directly cast into anodes for further gold electrowinning. Therefore, measures must be taken to reduce the excess silver content and improve the purity of the gold.
There are two main methods for achieving this:Acidic Dissolution Method:The anode slime is immersed in nitric acid, allowing the dissolution of the excess silver while keeping the gold largely undissolved. The solution is then separated into solid residue (containing high-purity gold) and liquid extract (for recycling the dissolved silver). The residual solid can then be cast into anodes for electrowinning.
Second Electrowinning Process:The anode slime is melted into anodes, which are then subjected to a second round of electrowinning to further reduce the silver content. This step improves the gold concentration in the anode slime, often achieving purity levels above 90%.
Additionally, after dissolving excess silver using nitric acid, alternative methods such as King's Water or Chloride Leaching can be employed to recover gold from the solid residue. These methods include water-based and chloride-based gold leaching techniques, both of which are widely used in industrial applications.
-
 Recovering Platinum Group MetalsMethods for Recovering Platinum Group Metals from Used Catalysts
Recovering Platinum Group MetalsMethods for Recovering Platinum Group Metals from Used CatalystsMethods for Recovering Platinum Group Metals from Used Catalysts
Recovering platinum group metals (PGMs) from used catalysts can be achieved through various methods, each offering its own set of advantages and challenges. Below is a summary of these methods along with key considerations:
High-Temperature Volatilization Method:This method involves controlled high temperatures to vaporize PGMs in their oxidized or chlorinated forms. Specialized equipment, such as absorbing devices, is used to collect the volatile metals. Challenges include the need for precise temperature control and potential costs associated with this equipment.
Carrier Dissolution Method:Strong acids (e.g., HCl, H₂SO₄) or bases (e.g., NaOH) are used to dissolve aluminum oxide carriers, leaving PGMs in sludge. While straightforward, this method may leave residual metals requiring further processing.
Selective Dissolution Method:Solvents are employed to selectively dissolve PGMs without fully dissolving aluminum oxide. This approach holds promise for selective extraction, though the effectiveness and reusability of the solvents require verification.
Full Dissolution Method:Involves completely dissolving both carriers and PGMs into a solution, followed by leaching or ion exchange to recover the metals. While efficient, this method may lead to contamination if not handled properly.
Furnace Melting Method:Metals are separated based on their melting points under high-temperature conditions. PGMs typically have higher melting points than aluminum, aiding in their separation. This method requires careful temperature control for complete recovery.
Burning Method:Specifically tailored for carbon-containing catalysts, this method burns the used catalyst to produce slag, which is then leached using water or hydrochloric acid to extract PGMs. Less energy-intensive but may not be suitable for all catalysts.
Considerations:Integration: Each method may necessitate preprocessing and combination with others for complex catalysts.
Cost-effectiveness: Methods like full dissolution or selective dissolution may have higher upfront costs but offer efficiency in recovery.
Scalability: We need to assess which methods can handle large volumes without losing efficiency.
Environmental Impact: Evaluating toxic byproducts and waste streams for sustainable disposal is crucial.
Conclusion:An optimal approach likely involves a tailored combination of techniques suited to the specific nature of the used catalyst. Further research and development are essential to enhance efficiency and sustainability in PGM recovery processes.







