 +8613303827570
+8613303827570
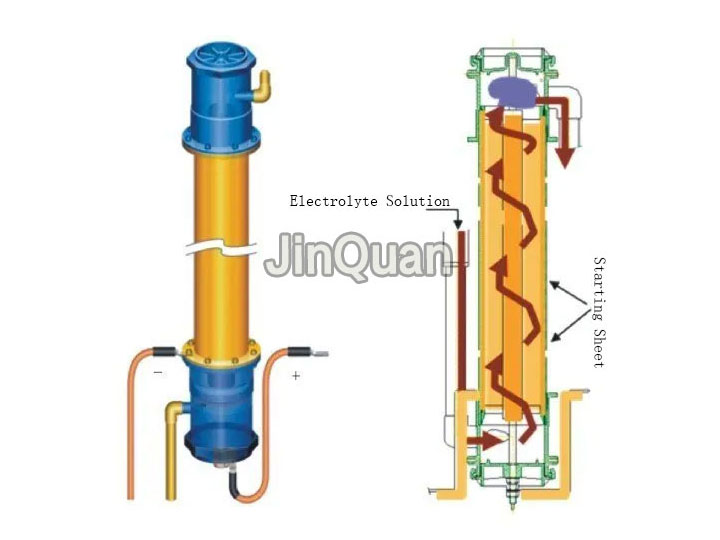
Rotating Electrode Technology and Conventional Electroplating Technology share the same electrochemical theoretical foundation. Both involve immersing the anode and cathode in an electrolyte solution containing target metal cations, achieving directed movement of ions under electric fields to deposit the target metal on the cathode.
The difference lies in that rotating electrode devices allow for higher flow velocity of the electrolyte solution, effectively utilizing the rapid flow of the electrolyte to eliminate concentration polarization phenomena during the electroplating process. This ensures more complete reaction and high purity of cathodic products with high current efficiency. It is particularly suitable for (wet metallurgical industry) in the selective electrolysis (electroplating) separation and purification of low-concentration and multi-component electrolyte solutions, or for removing metal ions from wastewater.
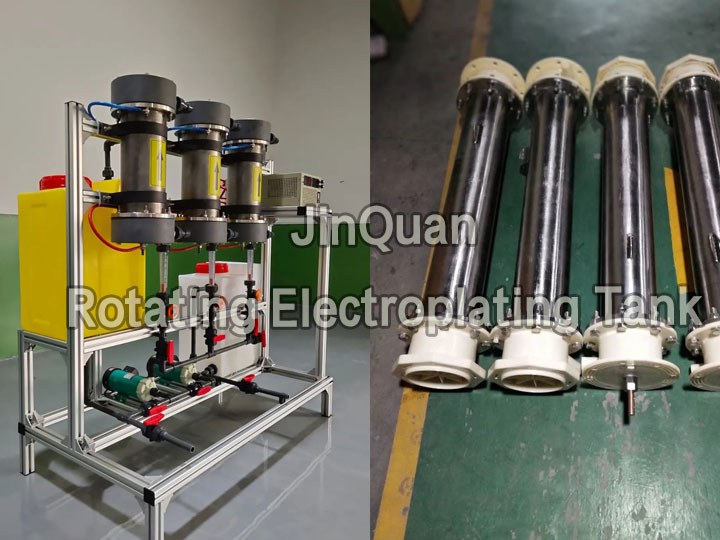

Applications:
1、Copper refining waste liquid purification;
2、Copper corrosion solutions copper recovery;
3、Zinc smelting slag copper and nickel recovery;
4、Copper, cobalt, nickel, zinc mixed metal ion solution copper, cobalt, nickel recovery;
5、Cyano solutions electrorefining Au and Ag recovery。
-
 Copper from High-Grade ChalcociteMethod for Enhanced Extraction of Copper from High-Grade Chalcocite
Copper from High-Grade ChalcociteMethod for Enhanced Extraction of Copper from High-Grade ChalcociteMethod for Enhanced Extraction of Copper from High-Grade Chalcocite
The method for enhanced extraction of copper from high-grade chalcocite belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy of non-ferrous metals. The high-grade chalcocite ore is crushed and formed into heaps. After heap construction, circulating leaching operations are performed using bacteria-containing raffinate with high acid and high iron content. The leachate is periodically sampled to analyze copper concentration; when the copper concentration in the leachate exceeds 3.5 g/L, the leachate is extracted for solvent extraction, and the raffinate after extraction is returned for continuous leaching.
By combining biological heap leaching circulation with acid return from extraction, a leaching system with high acid and high iron content is established in the high-grade chalcocite heap leaching process. This enhances and accelerates the rapid leaching of chalcocite, thereby shortening the leaching cycle, enabling large-scale copper leaching, and improving the utilization rate of copper resources.
-
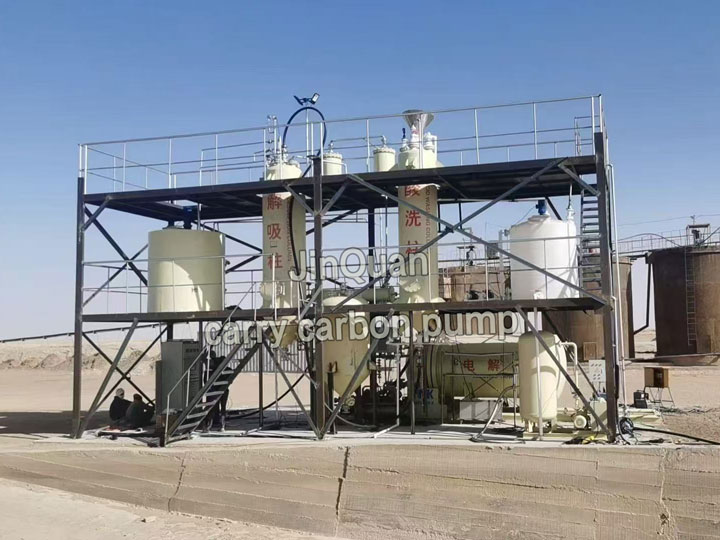
 Leaching refractory gold oresChlorination-Oxidation Leaching of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore
Leaching refractory gold oresChlorination-Oxidation Leaching of Gold from Refractory Gold OreMethod for Synergistic Chlorination-Oxidation Leaching of Gold from Refractory Gold Ore:
This method for synergistic chlorination-oxidation leaching of gold from refractory gold ore belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy.
First, crush the gold ore into ore powder; fully mix the ore powder, sodium hydroxide, sodium hypochlorite and water to obtain ore slurry; introduce air into the slurry, and perform ultrasonic-enhanced leaching under stirring conditions.
During the enhanced leaching process, hydrogen peroxide is added periodically. The synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydroxide is utilized to carry out redox reactions—their combined oxidation effect far exceeds that of either agent alone.
This not only shortens the reaction time but also improves gold leaching efficiency, saving reagent costs while boosting overall ore leaching performance. The leaching rate can reach over 98% using this method. Using sodium hypochlorite as the leaching agent does not impose environmental pressure; additionally, this invention adopts a one-step enhanced leaching process, simplifying the leaching workflow.
-
 The gold extraction processThe gold extraction process from copper-bearing oxidized gold ore
The gold extraction processThe gold extraction process from copper-bearing oxidized gold oreThe gold extraction process from copper-bearing oxidized gold ore falls under hydrometallurgical technology. First, the copper-bearing oxidized gold ore undergoes crushing, grinding and classification, followed by alkaline treatment. Then, a certain proportion of chelating agent and sodium cyanide are added to inhibit copper leaching and realize selective gold leaching. Finally, gold is extracted from the leachate via conventional activated carbon adsorption.
This method boasts a simple process, uncomplicated equipment and ease of implementation, along with high gold leaching rate, low reagent consumption, minimal capital investment and low cost. It is a gold extraction approach that is easy to industrialize and delivers good economic benefits.







