-
 recycling precious metals from circuit boards
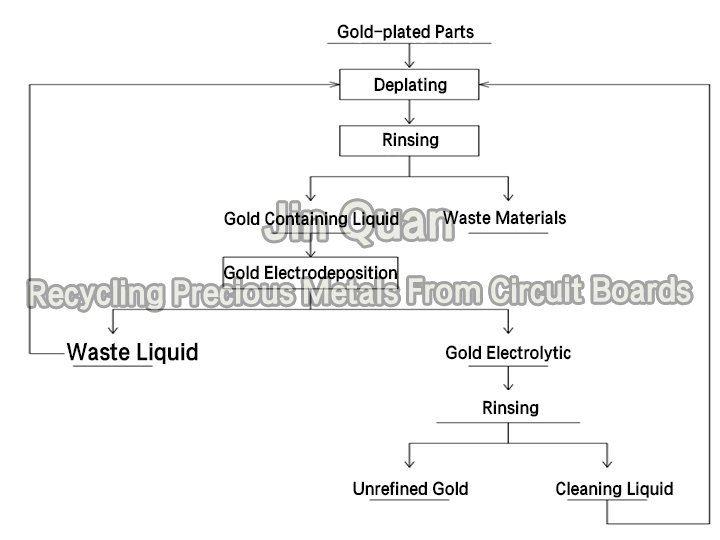
recycling precious metals from circuit boardsRecycling Precious Metals From Circuit Boards Process Description:
1)After the gold plating waste is loaded into the drum , the drum is lifted to the working position of the deplating tank (level 1 deplating tank) by a crane, and the motor is started to rotate the deplating tank.
2)After the deplating is completed, lift and drain the drum, then rinse it and enter the second level cleaning tank. Afterwards, dry it according to the actual situation.
3)After multiple de deplating processes, the gold content in the de plating solution reached a certain concentration (1.5g/L), and the solution was electrodeposited to recover gold. After electrodeposition, the gold content in the solution decreased to 0.4mg/L.
Recycling Precious Metals From Circuit Boards Process Diagram:
-
 extraction of precious metals from waste circuit boards
extraction of precious metals from waste circuit boardsMainly using methods or based on the differences in physical properties between materials, including density, conductivity, magnetism, surface characteristics, etc. for recycling, including processes such as disassembly, crushing, and sorting. Physical processing technology can enrich valuable substances in electronic waste, with advantages such as low cost and low pollution. However, due to the low proportion of precious metals in the total mass of printed circuit boards, it is difficult to recover high-purity precious metals using general methods. Various physical processing technologies still require subsequent processing of precious metal products. The main physical recycling methods currently used include impact crushing, extrusion crushing, shear crushing, high-speed eddy current crushing, dry screening, air shaking table, magnetic separation, electrostatic separation, pneumatic eddy current separation, and eddy current separation.
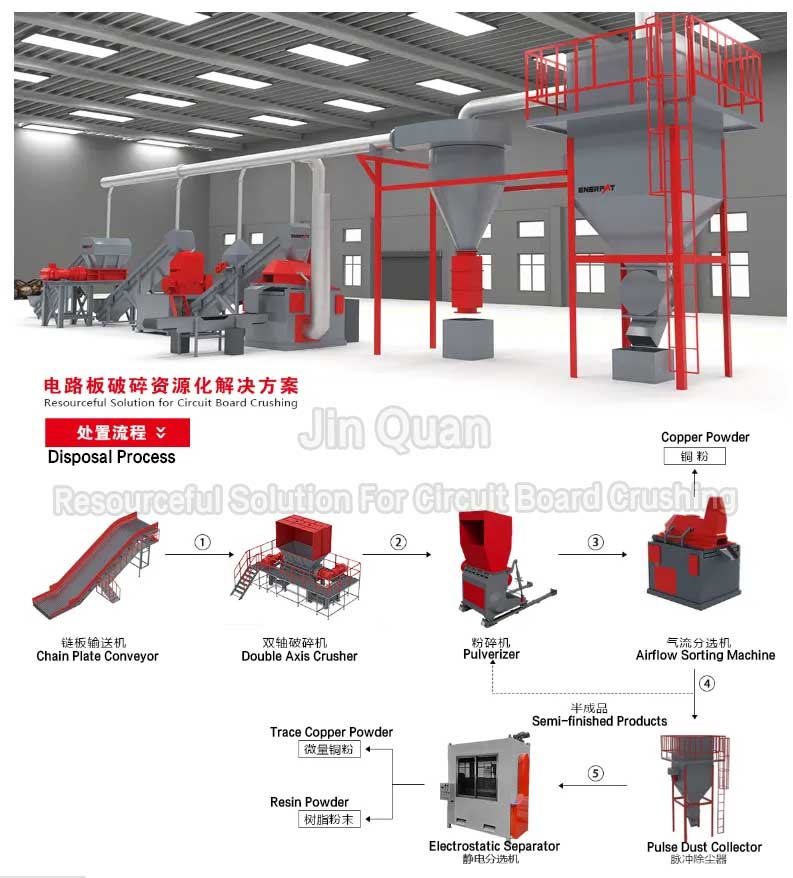
Resourceful Solution For Circuit Board Crushing: