-
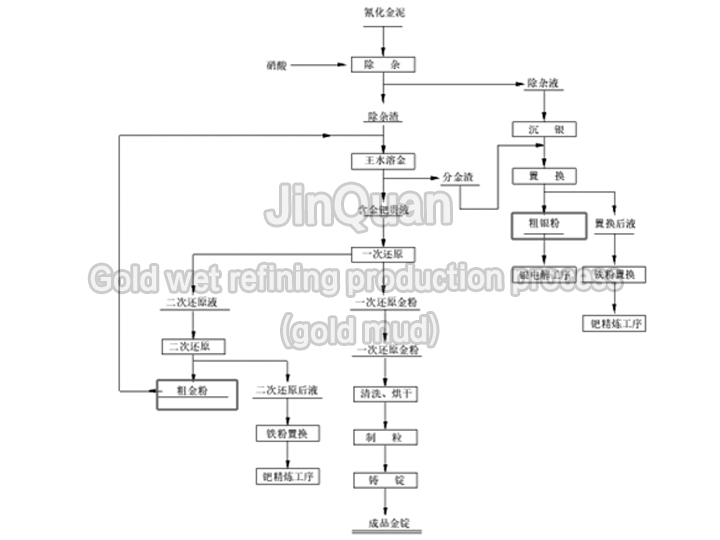 wet method refining gold production process (gold mud)
wet method refining gold production process (gold mud)Wet Method Refining Gold Production Process (gold mud)
Separation of Silver: Nitric acid is used to remove silver from gold, separating them.
Dissolution and Reduction of Gold: Sodium thiosulfate solution dissolves and reduces the gold from its compounds.
Post-Reduction Processing of Mercury and Platinum Group Metals (PGM): After reduction, mercury and platinum group metals are separated through a roughing process to isolate the PGMs from the filter residue.
-
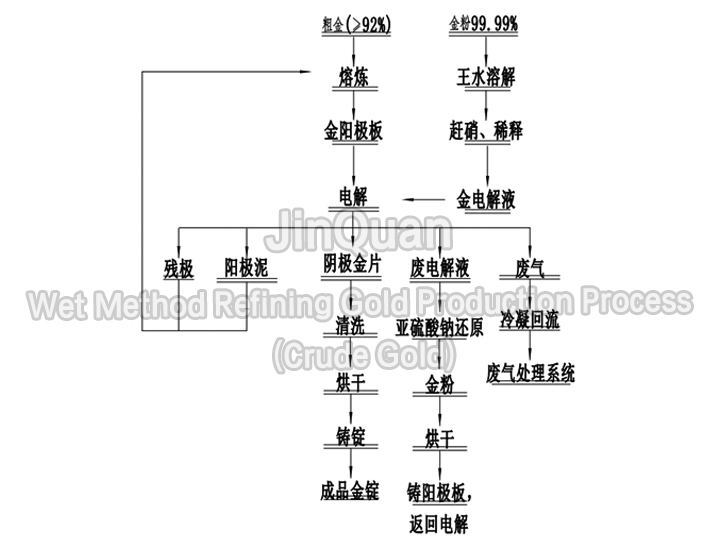 wet method refining gold production process (raw gold)
wet method refining gold production process (raw gold)Wet Method Refining Gold Production Process (Crude Gold)
Using raw gold as raw material, the process involves powderization, acid cleaning, and a single reduction to achieve gold with a purity of 99.95% or higher in one step. A second reduction is required for the refined gold powder, which needs to be re-dissolved to reach a purity of 99.5% or higher.
The acid cleaning solution requires to chlorinate silver precipitation, and the resulting filter residue undergoes iron powder substitution.
-
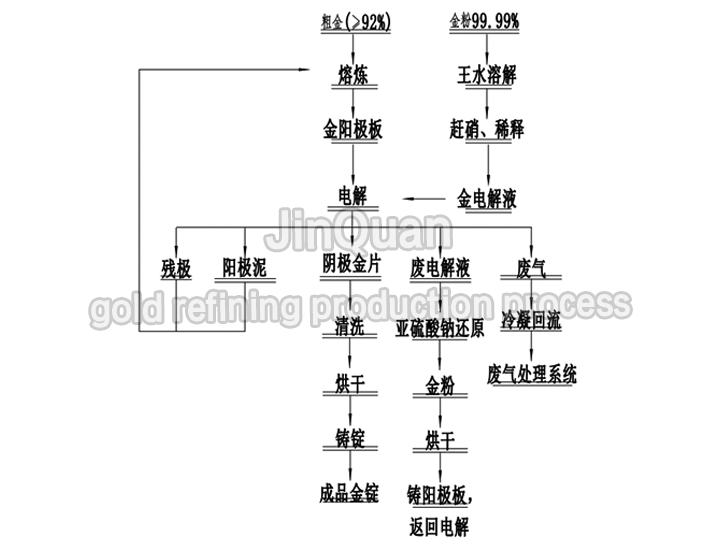 gold refining production process
gold refining production processRefining Gold Electrolytic Production Process
Using crude gold as the anode, employing a high-current-density electrolysis technology, produces stable electrolytic deposits of gold with a purity of 99.99% or higher on the cathode.
The anode is re-melted for recycling in electrolysis after cleaning.
High-gold anode residue is cast for recasting, and the platinum-tantalum residues in the anode residue are recovered using wet methods.
-
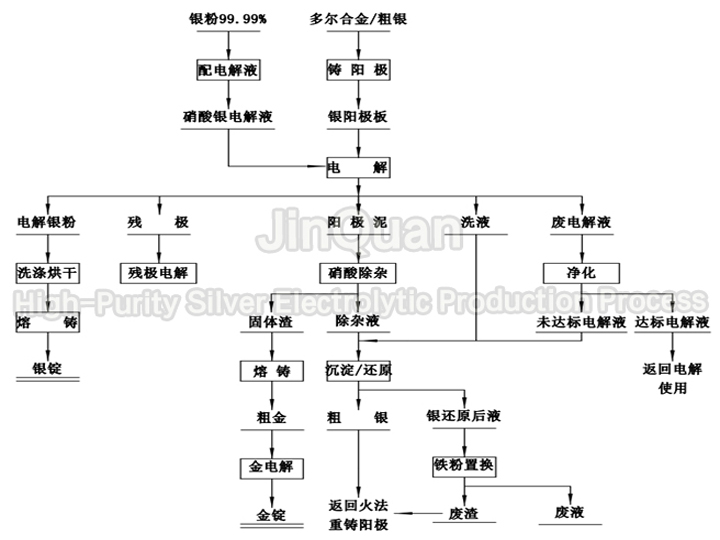 high-purity silver electrolytic production process
high-purity silver electrolytic production processHigh-Efficiency High-Purity Silver Electrolytic Production Process
Using either a Dore metal or crude silver as the anode and silver nitrate (AgNO3) as the electrolyte, employing a high-current-density electrolysis technology, produces silver powder with a purity of 99.99% or higher.
After cleaning the anode, it is directly placed into the anodic electrolytic cell to produce silver powder with a purity of 99.99% or higher.
Waste electrolyte undergoes oxidized silver purification, achieving purified electrolyte standards before recycling for reuse in electrolysis.
-
 mud pressure leaching-kaldor furnace treatment process
mud pressure leaching-kaldor furnace treatment processcopper anode slime mud pressure leaching-Kaldor furnace treatment process
Step-by-step recovery of silver, selenium, and tellurium from copper anode slime leaching solution;
Carlton furnace melting produces lead-bismuth slag, tellurium slag, and dore alloy.
-
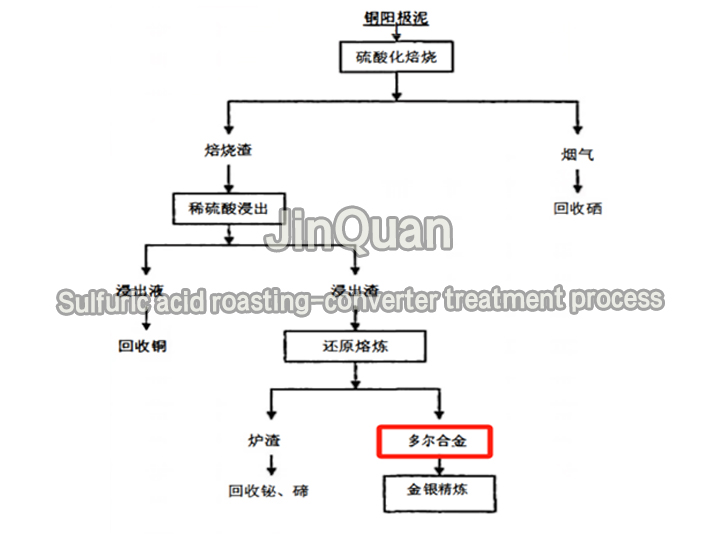 sulfuric acid roasting-converter treatment process
sulfuric acid roasting-converter treatment processSulfuric acid roasting-converter treatment process
Cu slag sulfurization roasting: High-temperature sulfurization roasting of selenium with forced cooling to capture selenium.
Acid leaching of copper: Copper solutions are settled with silver and copper precipitated.
Furnace reduction smelting, removal of lead, bismuth, tin, and tellurium, and processing of dore alloy.
-
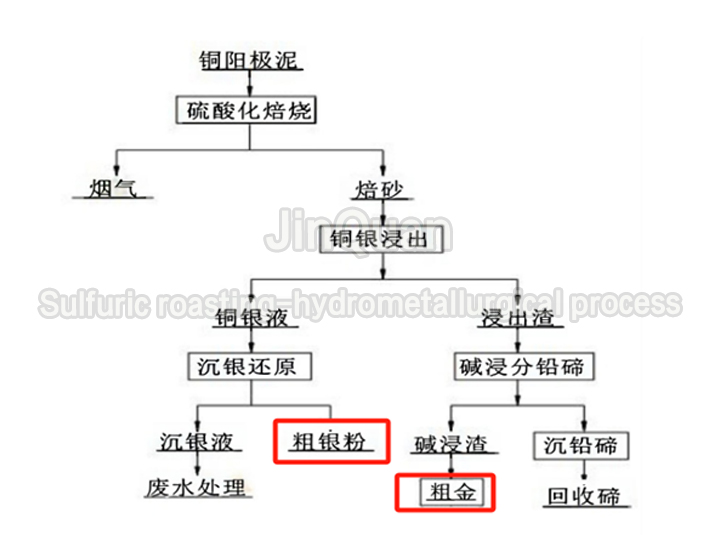 recovery method for valuable metals in copper anode slime
recovery method for valuable metals in copper anode slimeSulfuric roasting-hydrometallurgical process
Cu slag leaching: The first leaching removes copper and arsenic; the second leaching removes bismuth and tin.
Copper separation: Copper solutions are settled with silver and recovered of coltan.
Gold separation: Since the recovery of coltan is canceled, gold is separated from the gold solution in stages along with palladium and platinum.
Silver separation: Sodium sulfide and ammonia (ammonia gas) are used for silver separation. -
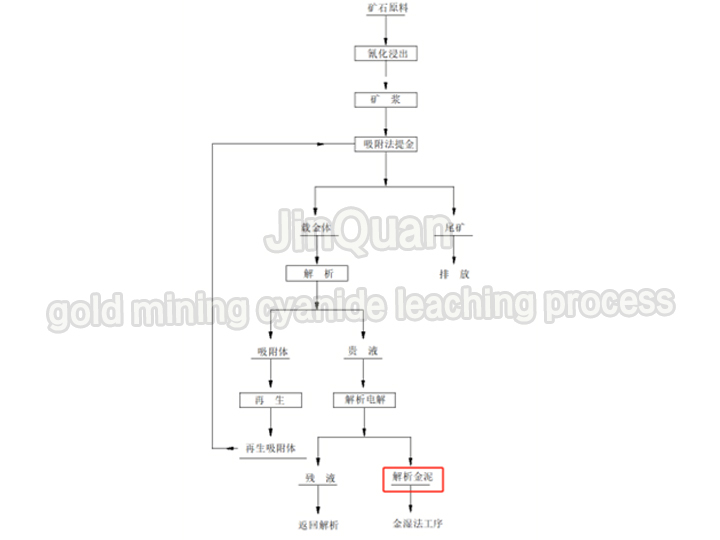 gold mining cyanide leaching process
gold mining cyanide leaching processgold mining cyanide leaching process
Cyanide leaching: The gold is separated from most minerals using cyanide, resulting in a gold-bearing slurry.
Activated carbon adsorption: Activated carbon absorbs gold from the cyanide solution.
Activated carbon desorption: The absorbed gold is removed from the activated carbon.
Electrorefining: The gold-bearing solution undergoes electrorefining to produce refined gold.
Refining: The refined gold goes through wet processing to achieve higher purity.
-
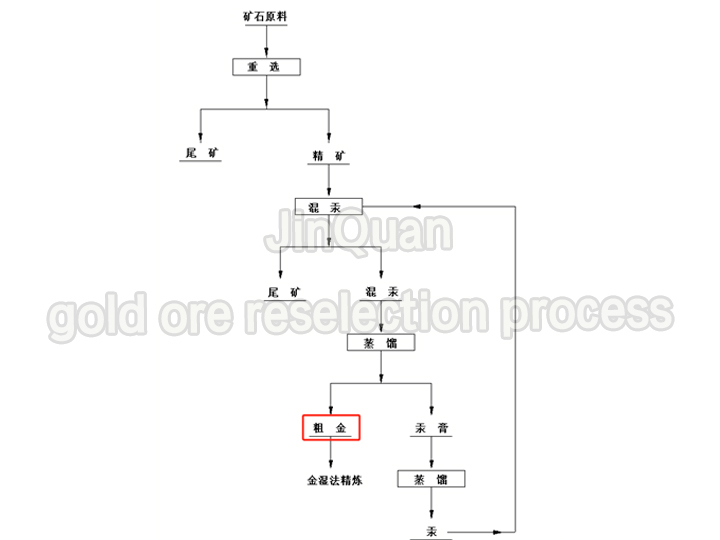 gold ore reselection process
gold ore reselection processgold ore reselection process
reselection: Separates gold from most minerals.
parting: The concentrate obtained is refined further through methods like vaporization to increase gold content.
refining: The refined dore goes through wet processing to achieve higher purity.







